The occurrence of neonatal diarrhoea can be contributed to by numerous factors and involve a number of pathogens including Escherichia coli and Clostridium perfringens (Kongsted et al, 2018). Neonatal diarrhoea causes significant economic losses and increased use of antimicrobials in the farrowing house. Estimated costs for herds affected by neonatal diarrhoea with mortality of 10% can be as high as €134 per sow per year. Together with swine dysentery, neonatal diarrhoea is the most expensive enteric issue on pig farms (Sjölund et al, 2014). C. perfringens Type A (CpA) has been recognised in numerous studies as one of the most important pathogens in causing neonatal diarrhoea and therefore focus has been placed on effective control of the bacteria. Correct diagnosis can be complex and require a combination of methods, but it is important to get this right to ensure the correct control methods can be implemented. Vaccination is one control method that will be discussed in this review, with studies showing good efficacy of vaccines containing both the alpha (CPA) and beta2 (CPB2) toxins (Fricke et al, 2021), which are suggested to play a role in the virulence of CpA (Waters et al, 2003).
The pathogen
C. perfringens is a Gram-positive rod-shaped anaerobic bacteria that is classified into 5 types (A-E) based on the toxins it secretes, including the four main toxins alpha (CPA), beta (CPB), elipson (ETX) and iota (ITX) (Zeng et al, 2021), some of which are pathogenic and result in disease. All types of C. perfringens can also produce the beta2 (CPB2) toxin (Uzal et al, 2010), which is suggested to be important in C. perfringens Type A. C. perfringens enters the piglet via ingestion (Niilo, 1988), and subsequently infects the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). Infected sows can pass the pathogen to piglets when they suckle or it may be picked up from the environment, such as from contaminated farrowing pens. Once the pathogen is established in the GIT, it can start to produce the pathogenic toxins, which result in the negative impacts on animal health and productivity that will be discussed (Table 1).
Table 1. Activities of the toxins of Clostridium perfringens relevant to piglets
| Toxin | Activity |
|---|---|
| Alpha | Multifunctional phospholipase, universal production by animal isolates, membrane phospholipid hydrolysis, cytotoxic or lytic effect, haemolytic and necrotising with lethal effect |
| Beta | Mucosal necrosis, central nervous system signs, necrotising, lethal, gene cpb is plasmid borne |
| Beta 2 | Pore-forming, cytotoxic toxin, possessing similar biological activity like beta1 toxin, cytotoxic for different cell lines and lethal for mice, two forms exist: consensus and atypical, when consensus is exclusive for pigs and is more toxic |
Adapted from Songer and Post, 2005
Pathogenesis
Pathogenesis of infection caused by the clostridia group is characterised by mechanism of invasive diarrhoea, meaning the barrier function of the gut is affected by the pathogen, mainly Type C (CpC) in the case of C. perfringens. The mucosa is most seriously affected, with pronounced damage of all compartments, and mortality of affected piglets is regularly observed (Uzal and Songer, 2019). The different types of C. perfringens produce various types of toxins, which contribute to the pathogenesis of the bacteria (Table 2).
Table 2. Major toxins produced by Clostridium perfringens types affecting pigs
| Major toxins | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toxinotype | CPA | CPB | CPE | CPB2 |
| A | + | - | +/- | +/- |
| C | + | + | +/- | +/- |
Adapted from Uzal et al, 2010
Clostridium perfringens Type C
The C. perfringens Type C (CpC) pathogen is characterised by a short generation time which enables it to multiply to high numbers (approximately 108–109 bacterial cells per gram of intestinal contents). It attaches to jejunal epithelial cells at villous apices, consequentially resulting in desquamation and necrosis (Ohnuna et al, 1992), and this intensive necrosis is characterised by haemorrhage. A key factor in pathogenesis of CpC is the lethal and necrotising beta toxin (CPB), considered as a major toxin for CpC (Warrack, 1963). Disease may follow after alteration of intestinal microflora, as well as a result of reduced activity of protease and pancreatic secretion deficiency, contributed to by the presence of protease inhibitors in colostrum. Development of clinical infection is therefore more typical in very young piglets with immature development of the GIT.
Clostridium perfringens Type A
Pathogenesis of CpA is poorly understood but it is obvious that it is multifactorial. The disease is characterised by a high number of CpA in the jejunum and ileum, reaching 108–109 per gram of intestinal contents (overgrowth of pathogenic strain). In piglets, CpA causes enteropathy after this substantial multiplication (Johannsen et al, 1993). All strains of CpA produce the principal alpha toxin (CPA), although there is variability in the quantity of toxin produced (Bueschel et al, 2003). CPA is a phospholipase with a cytotoxic, haemolytic and necrotising effect and is the major toxin in type CpA infection. Usually mild lesions are developed, suggesting that type A enteritis is a rather secretory diarrhoea compared with CpC, and deep effects on different intestinal mucosa parts is not characteristic.
Role of beta2 toxin in pathogenesis
Beta2 toxin (CPB2) has been discovered in two forms — the consensus and atypical variant. The consensus type is characteristic for piglet diarrhoea and is the more toxic form of the toxin. Several authors suggest that CPB2 plays a role in the causation of the enteric infection in pigs, but also in other animal species (Bueschel et al, 2003; Waters et al, 2003). In the majority of cases of diarrhoea positive for C. perfringens, strains identified are positive for CPB2 (> 85%) (Herholz et al, 1999; Bueschel et al, 2003). Particularly high correlation was described for neonatal piglets, where >86% of piglets with enteritis were positive for CPB2 toxin gene compared with 11.1% in healthy pigs (Bueschel et al, 2003). Other studies support this, with 82% positivity in affected animals and none in healthy animals, as well as a significant association between CpA possessing the CPB2 toxin gene and diarrhoea in piglets being identified (Garmory et al, 2000). This suggests that the CPB2 toxin may play a key role in the pathogenesis of the disease.
Clinical signs and lesions
Clostridium perfringens Type C
In the case of CpC, piglets are affected during the first week of life, usually around 3 days of age, and it is uncommon in older pigs (Bergeland et al, 1966). Mortality rate varies between studies, but herd mortality can be around 50% (Hogh, 1967) with mortality rates over 83% within litters in some herds (Hogh, 1965). Continuous acute disease outbreaks on farm could be as a result of piglets not receiving enough colostrum (Songer and Uzal, 2005), management issues or disease.
The disease can be peracute, acute or chronic. In peracute and acute cases, the clinical signs are characterised by abdominal pain, depression and haemorrhagic diarrhoea (Songer and Uzal, 2005). In piglets affected by the peracute disease, depression can be quickly followed by death without the other clinical signs (Posthaus et al, 2020). Chronic cases are characterised by non-haemorrhagic diarrhoea and reduced growth (Posthaus et al, 2020), commonly affecting pigs 1–2 week old or older, and may result in death as a result of dehydration and secondary bacterial infections (Niilo, 1988). The diarrhoea in chronic cases is usually intermittent (Uzal and Songer, 2019).
At post-mortem examination the main lesions are commonly seen in the small intestine, mainly jejunum, however, lesions in the large intestine can be occasionally observed (Barker et al, 1993). The lesions consist commonly of intestinal and mesenteric hyperaemia; and fibrinonecrotic enteritis with emphysema and haemorraghic content in the intestine (Figure 1). Adhesions can develop between intestinal loops, and mesenteric lymph nodes are reddened (Songer and Uzal, 2005).
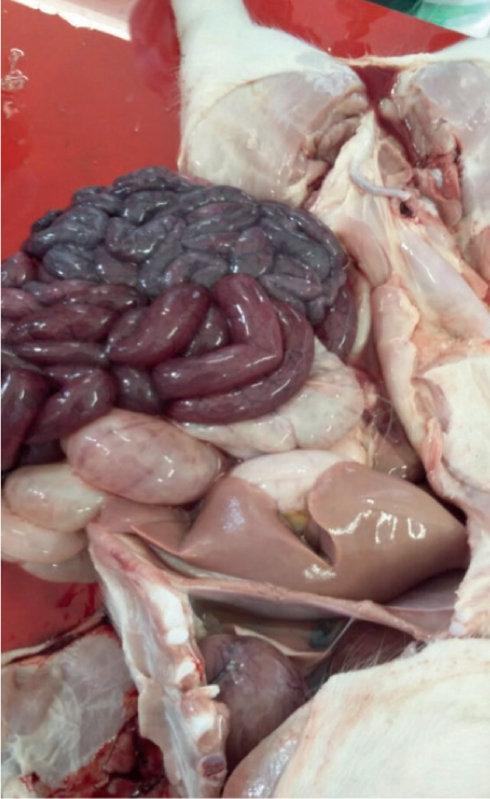
In piglets that survive the acute disease, the lesions that can be observed are dominated by fibrinous pseudomembranes and necrosis in the surface of the mucosa. This necrosis may extend to transmural intestinal necrosis with fibrinous peritonitis (Jaggi et al, 2009).
Clostridium perfringens Type A
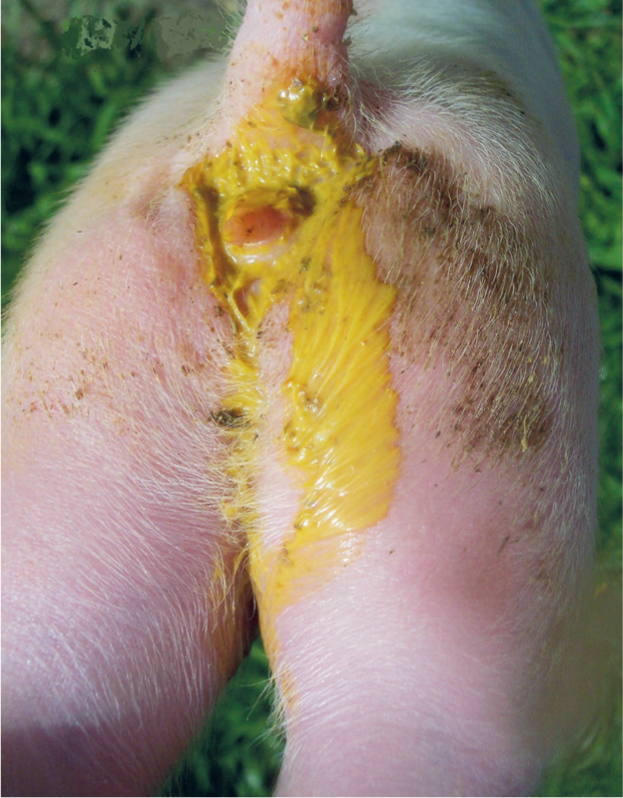
In cases of CpA the morbidity is high but the mortality usually remains low, with pre-weaning mortality rates of <10% (Collins et al, 1994). Although, high mortality has been reported in cases where severe diarrhoea is observed, caused by co-infection with E. coli (Wang et al, 2013). Any strain of this pathogen can cause enteric disease in neonatal piglets during the first week of life (Songer and Uzal, 2005). The main clinical sign is non-haemorrhagic mucoid diarrhoea in suckling piglets (Barker et al, 1993) (Figure 2). The diarrhoea is usually characterised by being foamy, fluid and yellow (Collins, 1989).
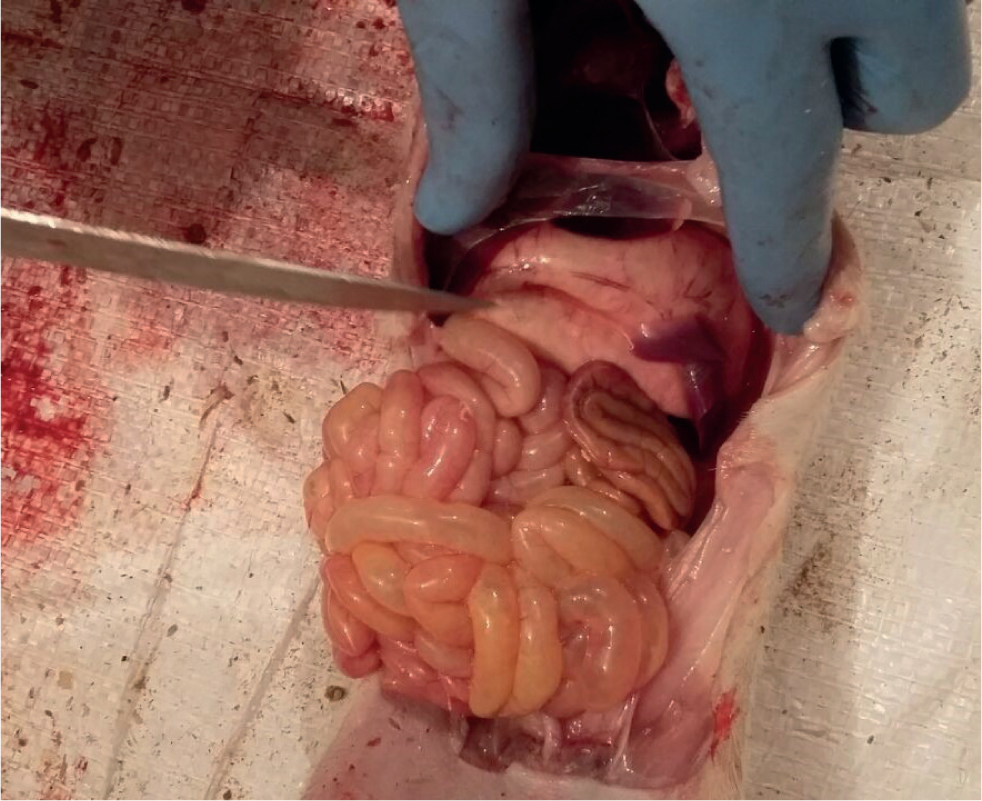
At post-mortem examination, lesions include mucosal necrosis and serositis; they are more severe in the small intestine, particularly the jejunum and ileum (Olubunmi and Taylor, 1985). It is common to find flaccid, thin-walled, gaseous, or watery small intestine and pasty colonic contents (Schwartz, 2009) (Figure 3).
Microscopical lesions
Histological lesions observed with peracute CpA include deep necrosis of the jejunal mucosa associated with marked haemorrhages into the lamina propria, submucosa and muscular layer (Miclard et al, 2009). Another common finding is necrosis of the small intestinal villi (Jaggi et al, 2009). Thrombosis and necrosis of small vessels in the lamina propria and submucosa can be observed consistently (Kohler et al, 1979; Johannsen et al, 1986).
In acute to subacute cases there is complete necrosis of the mucosa and infiltration with moderate to large numbers of neutrophilic granulocytes, and there is extensive necrosis within the lamina propria and submucosa (Miclard et al, 2009). Diffuse oedema can be seen throughout all intestinal layers with inflammatory cell exudate. Lesions in other segments of the intestine can occur and they are morphologically similar, however specific histological changes are not usually observed outside the gastrointestinal tract (Songer and Uzal, 2005).
In cases of CpA, Songer and Uzal (2005) described villus tip necrosis with fibrin and neutrophils, a fibrinonecrotic pseudomembrane and occasional serositis in a proportion of affected pigs. In other cases there are a lack of specific associated microscopic lesions (Collins, 1989).
Diagnostics
The diagnostic procedure starts with the identification of the characteristic clinical signs in infected piglets. These animals may show depression, listleness, weakness, lack of suckling, low body temperature and haemorrhagic diarrhoea in the case of CpC (Niilo, 1988). The mortality pattern can also be indicative (Songer and Uzal, 2005). In the case of CpA, the diarrhoea is non-haemorrhagic. The next step is to culture C. perfringens in the intestinal content or faecal samples. The pathogen is easily isolated by culture on blood agar and the isolation of a large number followed by genotyping of isolates can lead to a final diagnosis (Songer and Uzal, 2005) (Figure 4). Immunohistochemistry is not used as the method of choice for routine testing because of the quick degradation of the tissue caused by clostridial enzymes and autolysis from digestive enzymes (Posthaus et al, 2020).
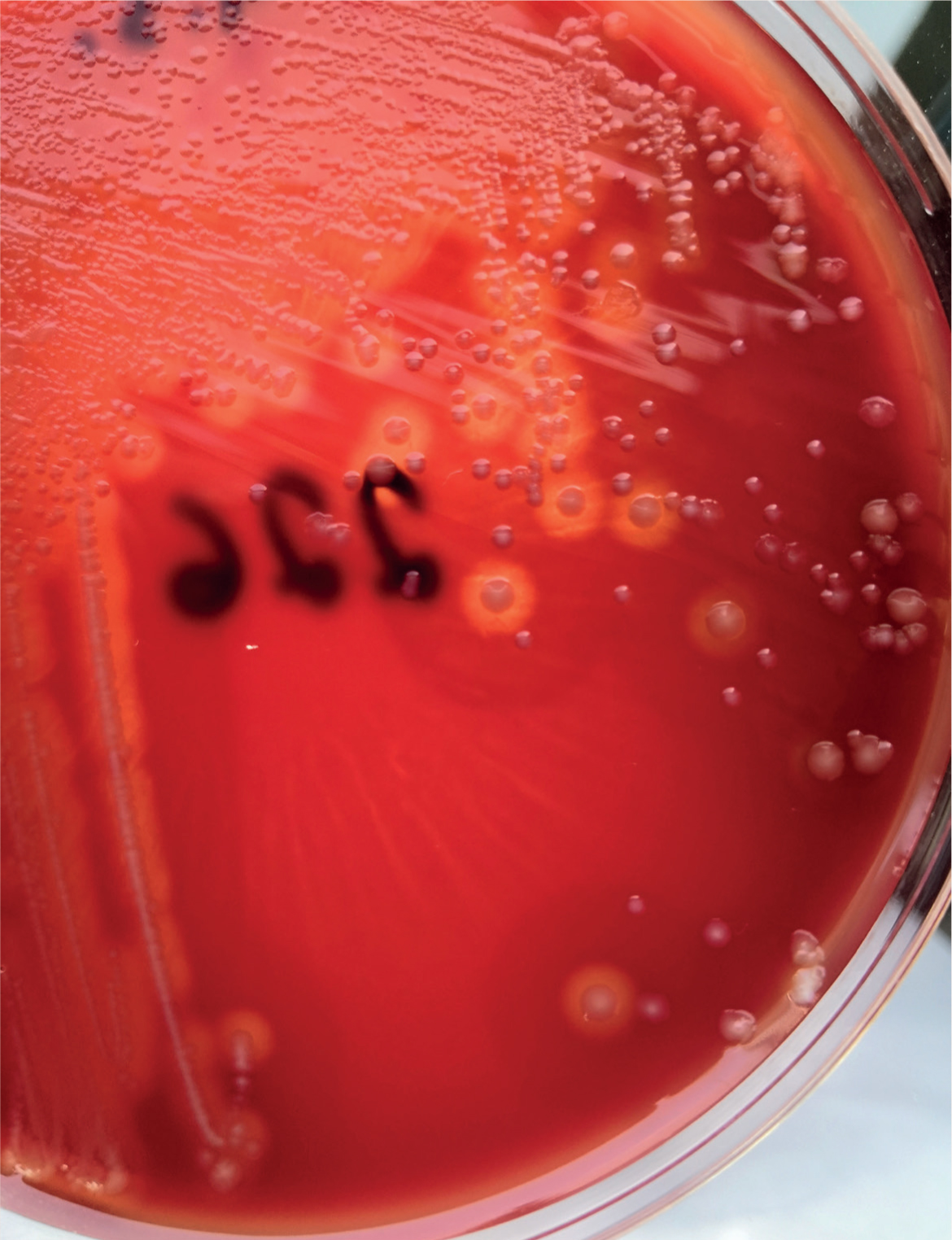
It is important to determine the toxin type to establish a complete diagnostic picture and identify the type of C. perfringens affecting the animals, especially as C. perfringens is part of the normal flora of the swine intestine (Mansson and Smith, 1962). Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) tests can be used to detect the secreted toxins in the samples (Posthaus et al, 2020), and the use of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods has replaced toxin detection assays in typing of isolates (Buogo et al, 1995; Songer and Meer, 1996). PCR methods are now used routinely to detect toxin-encoding genes to distinguish between Clostridium perfringens isolates (Moller and Ahrens, 1996).
Control measures
Control measures of neonatal diarrhoea are focused on management, especially focused around breeding stock in the gestation and post-farrowing period. As with many other disease prevention protocols, generating immune prophylaxis of breeding animals is among the methods that have shown to be effective in controlling the disease on farm. Body condition of sows in gestation period is important within this as it influences the ability to produce the optimal amount of colostrum and therefore should be focused on. Effective acclimatisation of gilts, and an all-in all-out management system, play an important role in control of neonatal diarrhoea in general. Piglets should be kept warm and be dried as soon as possible after farrowing, therefore drying material should be at hand in farrowing accommodation. Implementation of this strategy results in less energy expenditure for the piglets and allows sufficient colostrum intake during the first 24 hours of life (at least 150 g of colostrum per kg of live weight). In order to benefit from protective function of colostrum (especially after vaccination), optimum consumption needs to be controlled. It is essential to allow piglets to remain with their mothers for at least 24 hours after birth. Cabrera et al (2012) showed that piglets seemed to have 91% chance of survival until weaning, when their serum IgG concentration was between 23 and 25 g/litre at 48–72 hours of life.
Vaccination
Preventive medicine protocols focus on protection of piglets before weaning, involving the vaccination of gestating sows to induce passive transfer of antibodies and cellular immunity to the piglets via colostrum. Maternally-derived immunity is mainly based on colostrum ingestion during the first 24 hours of life but it can also be maintained at gut level with the ingestion of milk produced by vaccinated sows. Colostrum antibody titers are significantly higher in vaccinated sows and gilts (Fricke et al, 2021), and consequently improved protection is transferred to their piglets. Correct vaccination is vital to success as well as ingestion of sufficient colostrum by piglets.
The primary vaccination schedule is based on two shots, usually at 5 weeks and 2–3 weeks before the expected date of farrowing (Figure 5) (Kennedy et al, 1977). Regular booster vaccination before each farrowing is important in order to secure optimal level of antibodies with low variability in between the breeding animals.
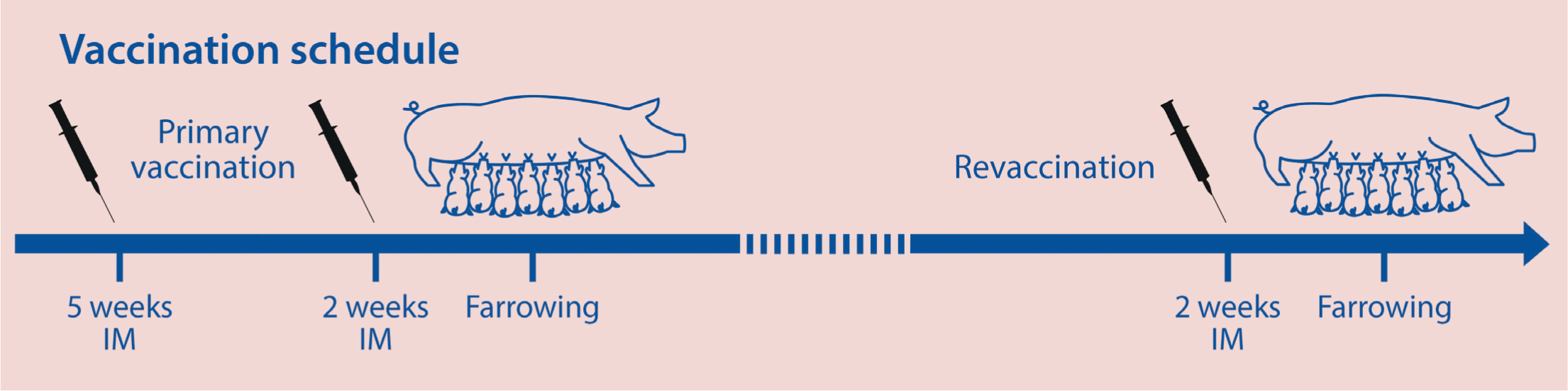
Vaccination against exotoxin producing bacteria is based on protection by the neutralisation of toxins. C. perfringens (CpC and CpA) is a typical exotoxigenic bacteria causing infection of new-born piglets based on production of major CPA and CPB lethal toxins, as well as CPB2 toxin in the case of CpA virulent strains. Toxins play an important role in the pathogenesis of infection in the first days of life of piglets and protection is based on passive transfer of antibodies from vaccinated mothers to progeny. Optimal antigenic composition of vaccines available for the control of mentioned pathogens is crucial. For example, vaccines based on CPB do not protect against CpA, as the CPB2 toxin is different from the CPB produced by strains of Type C (Uzal and Songer, 2019).
Conclusion
C. perfringens Types A and C both play a role in the clinical neonatal diarrhoea observed on pig farms worldwide. The pathogen produces toxins that cause changes to the gastrointestinal tract, which results in loss of productivity, therefore having an economic impact, as well as a negative impact on animal health and welfare. It is important that the pathogen is effectively controlled using a multifactorial approach including hygiene measures to reduce infection pressure and management measures such as vaccination of breeding stock. Vaccination of breeding stock with vaccines containing all the major toxins, such as CPA and CPB together with other important toxins such as CPB2, is important to ensure maximal protection.
KEY POINTS
- Clostridium perfringens is one of the most important pathogens involved in neonatal diarrhoea.
- Toxins produced, such as CPA and CPB2, are suggested to have a role in the virulence of the pathogen.
- Diagnosis of the pathogen, type and toxins involved in each case is important in ensuring the most effective control measures can be put in place.
- Vaccination of sows has been shown to be effective at reducing the impact of C. perfringens on farm.
- Vaccination is important to induce passive transfer of antibodies and cellular immunity to piglets via the colostrum.


